The Circulatory System
Oct 16, 2018 - Circulatory system, system that transports nutrients, respiratory gases, and metabolic products throughout a living organism, permitting.
Welcome to Medical News Today Healthline Media, Inc. Would like to process and share personal data (e.g., mobile ad id) and data about your use of our site (e.g., content interests) with our third party partners (see a ) using cookies and similar automatic collection tools in order to a) personalize content and/or offers on our site or other sites, b) communicate with you upon request, and/or c) for additional reasons upon notice and, when applicable, with your consent.
Healthline Media, Inc. Is based in and operates this site from the United States. Any data you provide will be primarily stored and processed in the United States, pursuant to the laws of the United States, which may provide lesser privacy protections than European Economic Area countries. By clicking “accept” below, you acknowledge and grant your consent for these activities unless and until you withdraw your consent using our. Learn more in our.
It's time you switched to a better browser For a better, secure browsing experience, we've made the tough decision to no longer support early versions of Internet Explorer (8 and below) and Firefox (22 and below). Unfortunately these older web browsers do not support many crucial developments in online security, and therefore represent a threat to your online security, as well as the security of MNT. For the safety and security of your online experience, we strongly recommend that you switch to a more modern browser (we've provided links to a few at the top right of the page). While you will continue to be able to read MNT as normal, your actual experience may not be exactly as we intended and you will not be permitted to log-in to, or register for an MNT account. Thank you, The MNT Team. Please accept our privacy terms We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your browsing experience, personalize content and offers, show targeted ads, analyze traffic, and better understand you.
We may share your information with third-party partners for marketing purposes. To learn more and make choices about data use, visit our. By clicking “Accept and Continue” below, (1) you consent to these activities unless and until you withdraw your consent using our rights request form, and (2) you consent to allow your data to be transferred, processed, and stored in the United States.
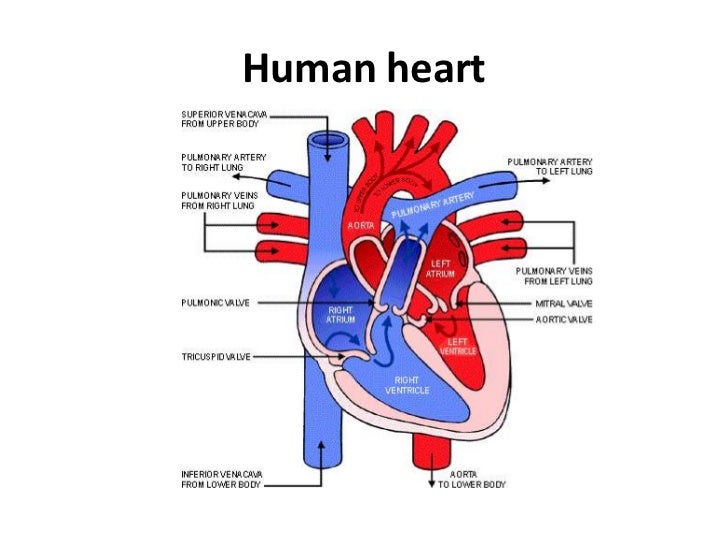
The blood circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart and the blood vessels that run throughout the body. It delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells of the body. The oxygen we breathe gets mixed into the blood in the lungs, and the heart pumps this blood to all parts of the body.
Each heartbeat is a contraction of the heart as it pumps blood around the body. The heart has four chambers: the left atrium, right atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle.
They are all separated by one-way valves, meaning the blood can only flow in one direction. Blood is carried to the heart in the veins, and back out to the rest of the body in the arteries.
There are many different circulatory system diseases all of which interrupt this complex process of distributing blood around the body. In this article, learn about diseases that affect the circulatory system, as well as treatment options and prevention. Fifteen circulatory system diseases. The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels. Diseases that can affect the circulatory system include: 1. Atherosclerosis is a hardening of the arteries.
It is typically caused by a diet high in fat, which leaves fatty deposits on the lining of the blood vessels. These fatty deposits stick together and make the arteries hard and less flexible. Atherosclerosis leads to, which can damage the heart and kidneys and even lead to. Heart attack Myocardial infarction (MI) is the technical term for a.
A heart attack can occur when the blood supply is cut off from the heart, often by a blood clot. Some heart attacks are minor, but others can be life-threatening. Mitral valve prolapse Mitral valve prolapse means the mitral valve bulges out or prolapses because it does not close evenly.
The mitral valve pumps freshly oxygenated blood out of the heart to the rest of the body. Mitral valve regurgitation Mitral valve regurgitation happens when the mitral valve does not close all the way and causes a leak, allowing some of the oxygenated blood to flow backward. Mitral stenosis Mitral stenosis means the mitral valve is abnormally narrow which can prevent the blood from flowing smoothly or quickly through it. Angina pectoris pectoris means 'pain in the chest' and occurs if the heart is not receiving enough blood. People often describe it as a crushing sensation or feeling like their chest is in a vice. People with angina pectoris may also feel breathless, tired, and nauseated. Arrhythmia and dysrhythmia and dysrhythmia are often used interchangeably, and both refer to abnormal heart rates and rhythms.
In general, arrhythmia means 'no rhythm' and dysrhythmia means 'abnormal rhythm.' High is usually caused by a sedentary lifestyle and an unhealthful diet. Some people can also be genetically at risk of high cholesterol. People need cholesterol, but too much cholesterol can form a thick layer on the inside of the vessels, blocking blood flow. Heart failure means that the heart is not pumping blood around the body as efficiently as it should. It can lead to, shortness of breath, and coughing.
Some people with heart failure find it difficult to do things such as walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries. High blood pressure (hypertension) High blood pressure or means the force or pressure of the blood flowing through the vessels is consistently too high.
High blood pressure can lead to stroke, loss of vision, heart failure, heart attack, kidney disease, and reduced sexual function. Stroke A stroke can happen when one of the vessels that lead to the brain either becomes blocked by a blood clot or bursts. This stops blood flow and prevents oxygen from getting to the brain. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) (PAD) refers to narrowing of the arteries that lead to the legs, stomach, arms, and head. This reduced blood flow can damage the cells and tissues in the limbs, organs, and brain. PAD tends to occur more often in older people. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a blood clot that gets stuck in a vein, blocking the flow of blood.
It is a serious condition that needs emergency medical attention. Aortic aneurysms Aortic affect the main artery in the body. It means the artery wall has weakened, allowing it to widen or 'balloon out.' An enlarged artery could burst and become a medical emergency.
The Circulatory System Is Composed Of
Various circulatory diseases are linked to one another. While scientists do not know what causes all of these diseases, there are things that individuals can do to reduce the risk of developing them. Many circulatory system diseases are linked to each other. For example, high blood pressure damages the blood vessels, which can lead to other circulatory problems. The narrowing of blood vessels caused by high cholesterol increases the likelihood of a person getting a blood clot.
Being overweight or obese also increases the possibility of developing circulatory diseases. However, a healthful diet and being active can reduce the risk. Regular exercise keeps the heart healthy by reducing the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and being overweight — all of which are risk factors for circulatory diseases.
People who have family members with a circulatory disease are more likely to develop one themselves. This risk, however, can be reduced with a healthful lifestyle. Does smoking increase the risk of circulatory diseases? Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing circulatory diseases. Toxic substances in tobacco can narrow and damage the blood vessels, increasing the risk of blood clots and causing poor circulation. When to see a doctor Some circulatory diseases, such as stroke, heart attacks, and burst aneurysms, are life-threatening and need emergency medical attention. Anyone who experiences heart pain is advised to make an appointment with their healthcare team.
People who are concerned that they are at risk of developing a circulatory disease can ask their doctor how to make healthful lifestyle changes. This content requires JavaScript to be enabled.
About cholesterol. (2018, January 11). Retrieved from Aorticaneurysm. Retrieved from Cardiovascular disease. (2016, September 7). Retrieved from Circulatory system diseases.
Retrieved from Health threats from high blood pressure. (2018, January 11).
Retrieved from How does the blood circulatory system work? (2016, August 1). Retrieved from Mitral valve prolapse. (2017, December 5). Retrieved from Mitral valve regurgitation.
(2017, September 7). Retrieved from Peripheral artery disease. Retrieved from Prevention. (n.d.) Retrieved from Silent ischemia and ischemic heart disease. (2016, September 19). Retrieved from Venous thromboembolism.
Retrieved from What is heart failure? (2018, March 7). Retrieved from. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: MLA Barrell, Amanda. 'What diseases affect the circulatory system?' Medical News Today.
MediLexicon, Intl., 1 May. APA Barrell, A.
(2018, May 1). 'What diseases affect the circulatory system?' Medical News Today. Retrieved from. Please note: If no author information is provided, the source is cited instead.
Recommended related news.
The Circulatory System: Multiple-Choice Questions Selected and approved by NSTA’s network of teacher-webwatchers Circulatory System What is the circulatory system? The body's breathing system The body's system of nerves The body's food-processing system The body's blood-transporting system From what source do cells get their food? Blood Oxygen Other cells Carbon dioxide Why is oxygen important to blood and to the cells? Oxygen helps the blood to clot. Oxygen brings food to the cells. Oxygen is necessary for cell growth and energy.
Oxygen is not important - carbon dioxide is the most important substance to the body. Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? Veins Arteries Capillaries Arteries, veins and capillaries Why is blood that flows from the lungs to the heart bright red rather than dark red? Oxygen makes it red. Carbon dioxide makes it red. Gastric juices produce the red colour of the blood. The lungs add a pigment (dye) to blood as it flows through them.
What part of the blood carries minerals, vitamins, sugar, and other foods to the body's cells? Plasma Platelets Red corpuscles White corpuscles What is the main job of the red corpuscles in the blood? To clot blood To fight disease To transport oxygen to the body's cells and carry away carbon dioxide from the cells To transport carbon dioxide to the body's cells and carry away oxygen from the cells Which of the following can best be compared to soldiers? Lungs Capillaries Red blood cells White blood cells Which element in the blood is round and colourless? Plasma Platelets Red blood cells White blood cells What would happen to people who have an open wound and whose blood did not clot naturally?
They may bleed to death. Clotting is not important. They would have to take regular doses of plasma. They would have to take regular doses of platelets. What happens when a clot occurred in an undamaged blood vessel? You would bleed to death.
A scab will form on the skin surface. Platelets stick to the edges of the cut and to one another, forming a plug. The flow of blood to tissues beyond the clot may be cut off.
What happens to blood when it is pumped into the thin-walled blood vessels of the lungs? Platelets are exchanged for plasma.
Carbon dioxide is replaced with oxygen. Blood fills the lungs and causes coughing. Nothing - the lungs are just a place blood goes through on its way back to the heart. What is the function of the blood vessels and capillaries? They pump blood to the heart. They filter impurities from the blood. They carry blood to all parts of the body.
The Circulatory System Summary
They carry messages from the brain to the muscles. Why does blood turn dark red as it circulates through the body? It starts to clot. It gets old and dirty flowing through the body. The oxygen in it is replaced with carbon dioxide.
The farther blood is from the heart, the more dark red it is. How many major types of blood have scientists discovered?
The Circulatory System For Kids
One: Type 'O' Two: white cells and red cells Three: white cells, red cells, and plasma Four: Types A, B, AB, and O What is the organ that pumps blood all throughout the human body? The lungs The heart The kidneys The blood vessels and capillaries How the heart works. The heart receives oxygen-deficient blood (see the white arrows) from the body into the right upper atrium. When the heart contracts, the right lower ventricle will pump the blood into the lungs, where the carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen.
After the exchange, the blood containing fresh oxygen flows into the left upper atrium. Oxygen-rich blood (see the black arrows) flows from the left upper atrium into the left lower ventricle. When the heart contracts, the left lower ventricle will force the blood out to the body through a network of arteries.